眠れなさそうな時に使ってる。ストレスを抱えると眠れなくなるタイプなんで(;^_^A朝起きても眠気を感じないから起きやすい。自分に合った睡眠薬だから手放せない。

左記クレジットカード、銀行振込、コンビニ決済に対応







更新日:2025/4/18
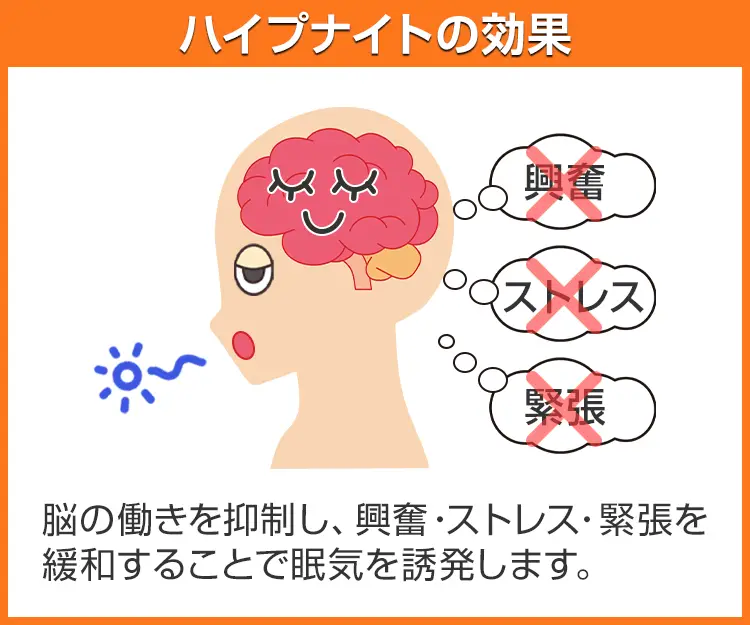
ハイプナイトは、日本でポピュラーな睡眠薬として認知されているルネスタのジェネリック医薬品です。
有効成分のエスゾピクロンは耐性がつきにくい性質があり、依存性が比較的低いという特徴があります。「飲んでいると依存してしまうのでは?」という不安なく使用できるのがメリットといえます。
| メーカー | コンサーン・ファーマ(Consern Pharma) |
|---|---|
| 有効成分 | エスゾピクロン |
| 効果 | 不眠症の改善 |
| 副作用 | 頭痛や味覚異常など |
| 用法 | 就寝直前に服用 |
エスゾピクロンは非ベンゾジアゼピン系に分類される有効成分で、脳を鎮静させるGABAを活性化させる作用があります。GABA-A受容体に作用することで効果を発揮します。
ハイプナイトには、含有量が異なる1mg錠、2mg錠、3mg錠の3種類があります。

| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50錠 | 60円 | 3,000円 | 90pt | |
| 100錠 | 55円 | 5,500円 | 165pt |
| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50錠 | 70円 | 3,500円 | 105pt | |
| 100錠 | 65円 | 6,500円 | 195pt |
| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50錠 | 80円 | 4,000円 | 120pt | |
| 100錠 | 75円 | 7,500円 | 225pt |






①1万円以上で送料無料
1回の注文で10,000円以上だった場合、1,000円の送料が無料となります。
まとめ買いをすると1商品あたりのコストパフォーマンスが高くなるためおすすめです。
②プライバシー守る安心梱包
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。

③100%メーカー正規品取り扱い
当サイトの商品は100%メーカー正規品となっており、第三者機関による鑑定も行っております。
商品の破損などがあった場合は再配送などにて対応させて頂きますので、ご連絡頂ければ幸いです。

④いつでも購入可能 処方箋不要
サイト上では24時間いつでもご注文を受けております。
また、お電話によるご注文も受け付けておりますのでネットが苦手な方はお気軽にどうぞ。

⑤商品到着100%
商品発送後はお荷物の追跡状況が分かる追跡番号をご案内させて頂きます。
郵便局には保管期限がありますのでご注意ください。
・自宅配達で不在だった場合の保管期限・・・16日間前後
・郵便局留めとした場合の保管期限・・・7~30日間

⑥コンビニ決済利用可能
ご近所のコンビニにていつでもお支払可能です。
セブンイレブンに限り店舗での機械操作を必要とせず、手続き完了後に表示されるバーコードや払込票番号をレジに提示することでお支払い頂けます。

ハイプナイト 1mg x 50錠
3,000円
ポイント:90pt
10,000円以上購入で送料無料
在庫あり

眠れなさそうな時に使ってる。ストレスを抱えると眠れなくなるタイプなんで(;^_^A朝起きても眠気を感じないから起きやすい。自分に合った睡眠薬だから手放せない。
初めは効いてたけど今は寝れなくなってきました。睡眠薬ってだんだん効かなくなるんですよねー。
主に寝つきが悪いタイプに高い効果があります。ですが、中途覚醒と呼ばれるタイプの不眠にも効果が認められています。すべての不眠症状に対して有効ではありませんが、寝付きが悪かったり夜中に目覚めるタイプには効果が期待できます。
成人では1回2mgの服用が原則ですが、症状に応じて増減することが可能です。通常、エスゾピクロンの最大服用量は3mgまでとなっているため、増量しての服用は可能ですが、時間差で追加してしまうと効果が目覚めてからも効果が残ってしまう可能性があるので注意してください。
不安を直接和らげる作用はありません。自然な眠りを促すことで結果的に眠りにつけないといった不安感が軽減される場合があります。その結果、不眠に伴う精神的ストレスの緩和にもつながることが期待されています。
就寝の直前に服用するようにしてください。ただし昼寝のような短時間の睡眠時には使用しないようにしてください。
新生児に影響を与える可能性があるため、服用は避けてください。
食事の影響をほとんど受けずに吸収されるため、空腹時でも服用可能です。ただし、胃への刺激が気になる人は軽い食事の後に飲むのも良い方法です。特に重い食事をとった後よりは、吸収がスムーズになると言われています。
突然服用を中止すると、一時的に眠れない日が続く「反跳性不眠」が起こることがあります。やめる際は、急に中止せずに徐々に減量する方法が推奨されています。
ハイプナイトには頻度は不明ですが依存性があるとされています。長期的な服用や急激な服用中止などによって生じることがあるため、医師に相談のうえご使用ください。
空腹時に服用するようにしてください。食後投与の場合、エスゾピクロンの血中濃度が低下する可能性があり、適切な効果を得ることができない可能性があります。
アルコールを摂取すると、眠気やふらつきが強く出たり、記憶障害(健忘)を起こすリスクが高まります。飲酒は薬の効果を不安定にするため、フルナイトを使う日はお酒を控えることが強くすすめられています。
はい、特に高齢者や体質、服用するタイミングなどによって、翌朝まで眠気や注意力の低下が続くことがあります。このため、朝に自動車の運転や機械操作など危険な作業は控えるようにすることが大切です。
| 1日の服用回数 | 1回 |
|---|---|
| 1回の服用量 | 1~3mg |
| 服用のタイミング | 就寝前 |
| 服用間隔 | 24時間 |
| 商品名 | フルナイト | ハイプロン | ソミナー | ソクナイト | アモバン・ジェネリック | デエビゴ | メラトニンタイムリリース | セディール |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品画像 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| 特徴1 | スムーズに入眠できる超短時間型の睡眠薬 | すみやかに入眠できる超短時間型 | ・入眠障害や中途覚醒を改善できる | 超短時間(2~4時間)のみ効果を発揮 | 入眠障害に効くアモバンのジェネリック | 中途覚醒を防いで自然な睡眠をサポート | ・自然に近い眠気を誘えるサプリメント | ・依存性や耐性が低い |
| 特徴2 | 作用時間が短く、翌朝に眠気が残りにくい | 寝覚めがよく眠気を引きずらない | ・アレルギー症状に対する効果も期待できる | ふらつきや転倒などが起きにくい | 翌朝に眠気を引きずらない | 依存性が比較的低い | ・フリーラジカルに対する効果も期待できる | ・気持ちを落ち着かせて快眠へ導く |
| 内容量 | 2mgx50錠 | 10mgx100錠 | 25mgx200錠 | 2mg50錠x1箱 | 7.5mgx30錠 | 5mg28錠x1箱 | 5mgx100錠 | 10mg42錠x1箱 |
| 価格 | 4,110円 | 4,590円 | 7,200円 | 4,110円 | 2,400円 | 15,800円 | 3,560円 | 5,850円 |
| 3%以上 | 1〜3%未満 | 1%未満 | 頻度不明 | |
| 精神神経系 | 傾眠 | 頭痛、浮動性めまい | 不安、注意力障害、異常な夢、うつ病 | 神経過敏、記憶障害、錯感覚、思考異常、感情不安定、錯乱状態 |
| 過敏症 | 発疹、そう痒症 | |||
| 消化器 | 味覚異常 | 口渇 | 口腔内不快感、口内乾燥、下痢、便秘、悪心 | 消化不良、嘔吐 |
| 肝臓 | AST、ALT、Al-P、γ-GTP、ビリルビンの上昇 | |||
| その他 | 倦怠感、湿疹、尿中ブドウ糖陽性、尿中血陽性 | リビドー減退、筋肉痛、片頭痛、背部痛、高血圧、末梢性浮腫 |
本製品は海外製のため、期限表記が日本と異なる場合がございます。
パッケージ裏面や側面、シートなどに以下のような表記がされています。
| EXP | 使用期限 例:EXP 12/2025→2025年12月まで使用可 |
|---|---|
| MFG または MFD | 製造日 例:MFG 03/2023 |
| BEST BEFORE | 品質が最も安定している目安日 |
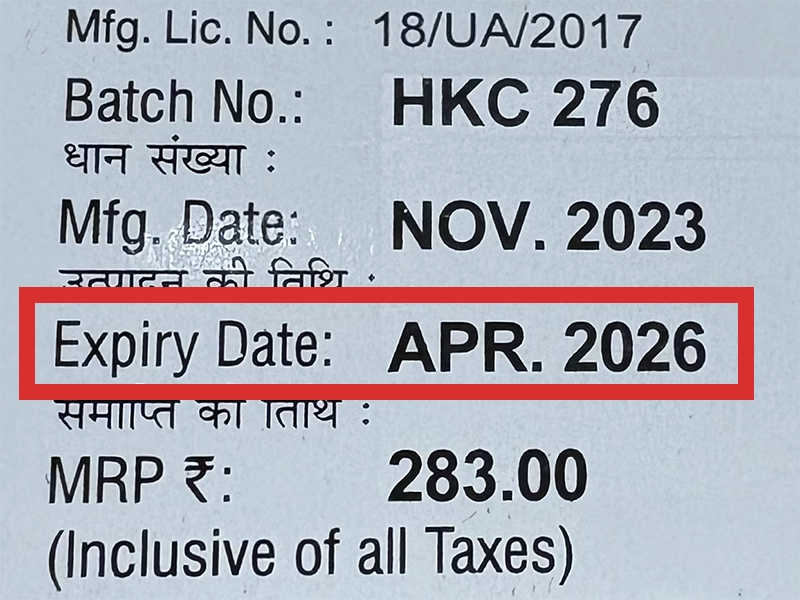
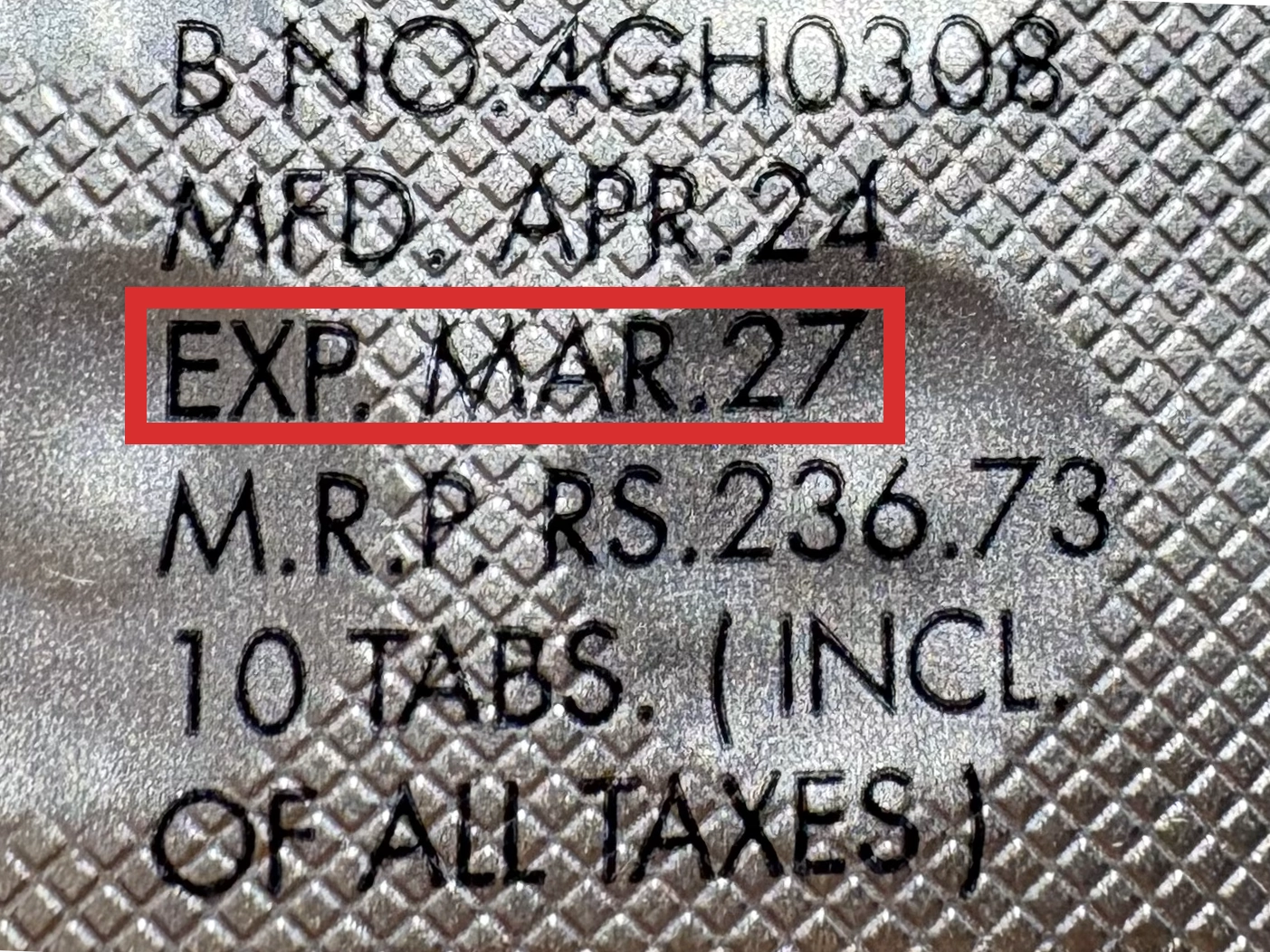
※国や製品により日付の並び(例:月/年、日/月/年)が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください
EXP(Expiry Date) の表記がなく、MFG または MFDしか記載がないケースがあります。
この場合は MFG(MFD) から2~3年が使用期限の目安です。
※「LOT」や「BATCH」の表記は製造番号であり期限ではありません。

パッケージ例となります。
商品やご注文単位によってはシート単位でのお届けとなる場合が御座います。
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。
服用してからベッドに入ると、ウトウトしてきてスムーズに眠る事ができます。不眠に悩んでいたことが嘘かのようです。依存性は少ないらしいので安心ですね。リピートしようと思います。
眠れなさそうな時に使ってる。ストレスを抱えると眠れなくなるタイプなんで(;^_^A朝起きても眠気を感じないから起きやすい。自分に合った睡眠薬だから手放せない。
私には効目が良く、副作用は気にならない程度です。今後も購入させてもらいます。
初めて睡眠薬に手を出します。依存性が少ないと書かれていたのが購入の決め手になりました。早く届いてくれると嬉しいです。
初めは効いてたけど今は寝れなくなってきました。睡眠薬ってだんだん効かなくなるんですよねー。
商品口コミの投稿は会員のみ行えるようになっております。
お手数ですが会員ログインの上でご投稿頂きますようお願いいたします。
口コミをご投稿頂いたお客様にはポイントをプレゼントさせて頂いております。
文章のみであれば100ポイント、文章+写真付きのものは300ポイントをプレゼントさせて頂きます。
規約や詳細などはこちらをご確認くださいませ。