なんでふつうに薬局で買えないのか不思議なくらい効きます!ここまで心が軽くなるのにもったいない!わたしはここで買えることを知れたので助かりました。

左記クレジットカード、銀行振込、コンビニ決済に対応



更新日:2025/4/17

| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50錠 | 83円 | 4,160円 | 124pt | |
| 100錠 | 50円 | 5,060円 | 151pt | |
| 150錠 | 42円 | 6,360円 | 190pt |






①1万円以上で送料無料
1回の注文で10,000円以上だった場合、1,000円の送料が無料となります。
まとめ買いをすると1商品あたりのコストパフォーマンスが高くなるためおすすめです。
②プライバシー守る安心梱包
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。

③100%メーカー正規品取り扱い
当サイトの商品は100%メーカー正規品となっており、第三者機関による鑑定も行っております。
商品の破損などがあった場合は再配送などにて対応させて頂きますので、ご連絡頂ければ幸いです。

④いつでも購入可能 処方箋不要
サイト上では24時間いつでもご注文を受けております。
また、お電話によるご注文も受け付けておりますのでネットが苦手な方はお気軽にどうぞ。

⑤商品到着100%
商品発送後はお荷物の追跡状況が分かる追跡番号をご案内させて頂きます。
郵便局には保管期限がありますのでご注意ください。
・自宅配達で不在だった場合の保管期限・・・16日間前後
・郵便局留めとした場合の保管期限・・・7~30日間

⑥コンビニ決済利用可能
ご近所のコンビニにていつでもお支払可能です。
セブンイレブンに限り店舗での機械操作を必要とせず、手続き完了後に表示されるバーコードや払込票番号をレジに提示することでお支払い頂けます。


うつ症状の改善
10mgx100錠
3,560円

うつ症状の改善
10mgx28錠
4,560円

うつ症状の改善
50mgx100錠
7,260円

うつ症状の改善
25mgx100錠
3,960円

うつ症状の改善
20mgx28錠
4,560円

うつ症状の改善
20mgx100錠
6,060円

うつ症状の改善
60mgx28錠
7,160円

うつ症状の改善
100mgx30錠
4,860円

うつ症状の改善
25mgx100錠
5,460円

うつ症状の改善
5mg28錠x1箱
4,860円

うつ症状の改善
20mg200錠x1箱
11,960円

うつ症状の改善
15mgx100錠
6,560円

うつ症状の改善
15mgx28錠
4,960円
トフラニール 25mg x 50錠
4,160円
ポイント:124pt
10,000円以上購入で送料無料
在庫あり

なんでふつうに薬局で買えないのか不思議なくらい効きます!ここまで心が軽くなるのにもったいない!わたしはここで買えることを知れたので助かりました。
長期間の服用に向いていないと書かれていたので、短期間と決めて飲んだのですが、それだけだと全然うつ病が治らないです。私のうつの症状がけっこう重症なのかもしれませんが、それでも少しくらいは効いてほしかったです。ただ、値段は他のうつ病用の薬と比較してもけっこう安いので、経済的には負担が無かったのは良かったと思います。今後どうするかはまだ検討中です。
トフラニールは、うつ病やうつ状態などに効果のある薬です。心の不調で気分が沈んだり、やる気が出ないときに、脳内の神経伝達物質(セロトニンやノルアドレナリン)のバランスを整えることで、症状をやわらげてくれます。
はい、気分の落ち込みや意欲の低下に対して効果があることが、複数の臨床試験で確認されています。うつ病患者の約64%で改善が見られたというデータもあります。気持ちが重く感じたり、何もやる気が出ないときに、その原因を脳の中から整えていく薬です。
トフラニールは、古くから使われてきた三環系抗うつ薬で、セロトニンだけでなくノルアドレナリンにも作用します。幅広い症状に効きやすいのが特徴です。新しい薬に比べて副作用は出やすい面もありますが、効果の強さと長年の実績が評価されています。
効果が感じられるまでには、1〜2週間ほどかかることが多いです。すぐに気分が変わるわけではないですが、続けて服用することで少しずつ改善していきます。あせらずに、医師の指示どおり続けることが、効果をしっかり引き出すポイントです。
はい、うつ病の治療では「継続」がとても大事です。症状が軽くなったように感じても、途中でやめると再発することがあります。トフラニールは、しっかり続けることで脳のバランスが整い、気分の安定が長続きしやすくなります。医師の指示に従って続けましょう。
トフラニールは基本的に1日2〜3回に分けて飲む薬です。時間帯は朝・昼・夜の食後など、生活リズムに合わせて処方されることが多いです。決まった時間にきちんと飲み続けることで効果が安定するので、医師や薬剤師に言われたタイミングを守るのが大切です。
眠気が強く出る場合は、夜にまとめる調整をすることもありますが、自己判断で時間や回数を変えるのはNGです。効き目が不安定になったり、副作用が強く出ることもあるため、気になる症状があるときは必ず医師に相談して飲み方を見直しましょう。
気づいたときにすぐ1回分を飲んでも大丈夫ですが、次の服用時間が近ければ1回分は飛ばしてください。2回分をまとめて飲むのは避けましょう。飲み忘れが続くと効果が落ちることがあるので、スマホのリマインダーなどを使って習慣化すると安心です。
よくある副作用には口の渇きや眠気、めまいなどがあります。特に飲み始めのころに感じやすく、体が慣れてくると落ち着くことも多いです。日常生活に支障が出るようなら無理せず医師に相談してください。早めの相談が大事です。
体重増加の副作用があらわれることがあります。食欲が増したり、炭水化物を欲しくなる傾向も報告されています。気になるときは、食生活や活動量を見直すとともに、医師に相談して調整することも可能です。
はい、トフラニールにはめまいやふらつきといった副作用が出ることがあります。特に立ち上がるときにクラッとする感じは「起立性低血圧」の可能性もあります。生活に支障がある場合は、医師に相談して服用量や時間を調整してもらいましょう。
トフラニールは他の薬と影響しやすいため、サプリや漢方、健康食品との飲み合わせにも注意が必要です。特にセントジョーンズワート(ハーブ)などは避けるべき成分です。新しく何かを飲む前には確認するようにしてください。
| 1日の服用回数 | 数回 |
|---|---|
| 1回の服用量 | 25~200mg |
| 服用のタイミング | 指定なし |
| 服用間隔 | 指定なし |
| 商品名 | インシドン | サミー | チアプリダール | サインバルタ・ジェネリック | ジェリフォルテ | キセパール | レクサプロ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品画像 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 特徴1 | ・神経伝達物質のバランスを整える | ・もともと体内にある天然物質を配合 | ・過剰なドパミンの神経伝達を抑える | ・安全性と有効性に優れた抗うつ剤 | ・免疫力の低下を防ぐ効果にも期待できる | ・優れた効果で精神症状を改善できる | ・世界的にも高い人気を誇る抗うつ剤 |
| 特徴2 | ・古くから使用される三環系抗うつ剤 | ・優れた抗酸化作用にも期待することができる | ・心を穏やかにする | ・イフェクサー・ジェネリックと同類薬 | ・天然成分が精神的な負担を軽減する | ・セロトニン系の神経にのみ作用するのが特徴 | ・不安な気持ちを軽減するためあがり症にも有効 |
| 内容量 | 50mg100錠x1箱 | 200mgx30錠 | 100mg20錠x1箱 | 20mgx100錠 | 100錠 | 40mg50錠x1箱 | 20mgx28錠 |
| 価格 | 9,160円 | 5,760円 | 3,960円 | 6,060円 | 2,860円 | 8,060円 | 9,960円 |
| 5%以上 | 0.1%〜5%未満 | 頻度不明 | |
| 循環器 | − | 血圧降下、頻脈、不整脈、動悸 | 起立性低血圧、心電図異常(QT延長等)、血圧上昇、心ブロック |
| 精神神経系 | パーキンソン症状・振戦・アカシジア等の錐体外路障害、眠気 | 運動失調、言語障害、知覚異常、幻覚、精神錯乱、攻撃的反応、激越、躁状態、不眠、不安、焦燥 | せん妄、ミオクロヌス、性欲減退 |
| 抗コリン作用 | 口渇、排尿困難、便秘 | 視調節障害(散瞳等)、鼻閉 | 眼内圧亢進、尿閉 |
| 皮膚 | − | − | 光線過敏症、脱毛 |
| 過敏症 | − | 発疹、そう痒感 | 顔・舌部の浮腫 |
| 血液 | − | − | 白血球減少、血小板減少、紫斑、点状出血、好酸球増多 |
| 肝臓 | − | − | AST、ALTの上昇 |
| 消化器 | 悪心・嘔吐 | 食欲不振、下痢、味覚異常 | 口内炎、舌炎 |
| 内分泌 | − | 体重増加 | 乳房肥大、乳汁漏出、体重減少 |
| 長期投与 | − | − | 口周部等の不随意運動 |
| その他 | ふらつき、めまい、発汗 | 倦怠感、脱力感、頭痛、異常高熱、熱感、耳鳴 | 血管痙攣、血糖値上昇、血糖値低下 |
本製品は海外製のため、期限表記が日本と異なる場合がございます。
パッケージ裏面や側面、シートなどに以下のような表記がされています。
| EXP | 使用期限 例:EXP 12/2025→2025年12月まで使用可 |
|---|---|
| MFG または MFD | 製造日 例:MFG 03/2023 |
| BEST BEFORE | 品質が最も安定している目安日 |
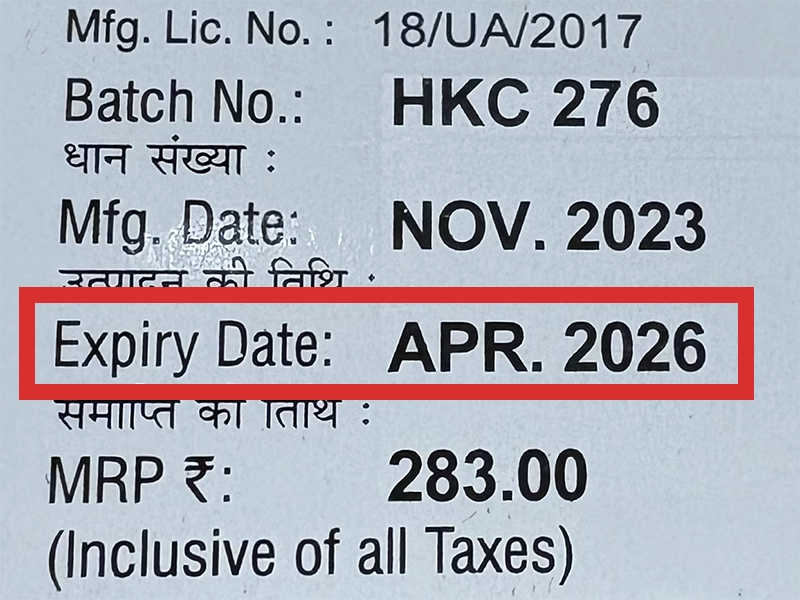
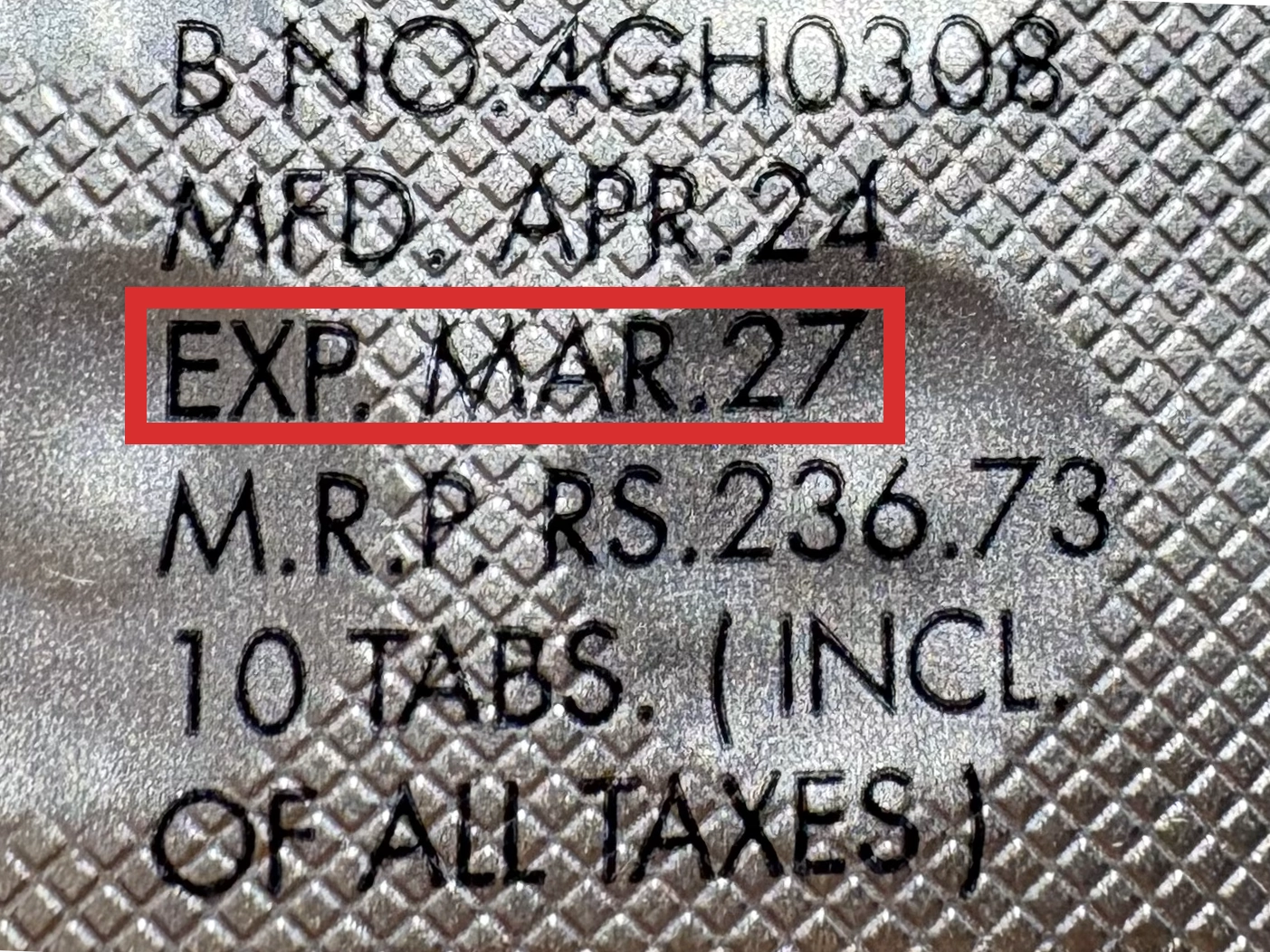
※国や製品により日付の並び(例:月/年、日/月/年)が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください
EXP(Expiry Date) の表記がなく、MFG または MFDしか記載がないケースがあります。
この場合は MFG(MFD) から2~3年が使用期限の目安です。
※「LOT」や「BATCH」の表記は製造番号であり期限ではありません。

パッケージ例となります。
商品やご注文単位によってはシート単位でのお届けとなる場合が御座います。
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。
なんでふつうに薬局で買えないのか不思議なくらい効きます!ここまで心が軽くなるのにもったいない!わたしはここで買えることを知れたので助かりました。
服用後、漠然とあった不安感が消えて穏やかな気持ちになります。ここまで気持ちが安定するのは久しぶりでした、これからはこちらを購入させてもらおうと思います。
前に飲んでいたものからこちらに切り替えました、こちらの方が自分には合うようでうつ症状がしっかり落ち着くのを感じる事ができました。助かっています。また購入させていただきます。
前に飲んでた抗うつ剤は頭痛を感じて飲みにくかった。これにしてみたら副作用は何も感じないし、効き目もあるからリピートしてる。薬代も安くなるから助かる。
精神科に行っても診察は秒で終わって、あとは薬を処方してもらって帰るだけ。移動時間の方が長い。行くのが面倒になってたから手軽に薬を買えるサイトを見つけられたのは嬉しい。海外輸入だから届くのに2週間前後はかかっちゃうけど、綺麗に届いたからよかった。また注文すると思う。
商品口コミの投稿は会員のみ行えるようになっております。
お手数ですが会員ログインの上でご投稿頂きますようお願いいたします。
口コミをご投稿頂いたお客様にはポイントをプレゼントさせて頂いております。
文章のみであれば100ポイント、文章+写真付きのものは300ポイントをプレゼントさせて頂きます。
規約や詳細などはこちらをご確認くださいませ。