いつも不安に押しつぶされそうで、次の日が来るのが怖くて眠れなかった。睡眠不足になって体調も優れないから薬を飲むようになった。今は不安な気持ちがどっかいって、落ち着いて過ごせるようになってる。眠るのも怖くない。今はこの薬を手放すのが怖い。

左記クレジットカード、銀行振込、コンビニ決済に対応





更新日:2025/4/3

| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100錠 | 72円 | 7,260円 | 217pt |






①1万円以上で送料無料
1回の注文で10,000円以上だった場合、1,000円の送料が無料となります。
まとめ買いをすると1商品あたりのコストパフォーマンスが高くなるためおすすめです。
②プライバシー守る安心梱包
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。

③100%メーカー正規品取り扱い
当サイトの商品は100%メーカー正規品となっており、第三者機関による鑑定も行っております。
商品の破損などがあった場合は再配送などにて対応させて頂きますので、ご連絡頂ければ幸いです。

④いつでも購入可能 処方箋不要
サイト上では24時間いつでもご注文を受けております。
また、お電話によるご注文も受け付けておりますのでネットが苦手な方はお気軽にどうぞ。

⑤商品到着100%
商品発送後はお荷物の追跡状況が分かる追跡番号をご案内させて頂きます。
郵便局には保管期限がありますのでご注意ください。
・自宅配達で不在だった場合の保管期限・・・16日間前後
・郵便局留めとした場合の保管期限・・・7~30日間

⑥コンビニ決済利用可能
ご近所のコンビニにていつでもお支払可能です。
セブンイレブンに限り店舗での機械操作を必要とせず、手続き完了後に表示されるバーコードや払込票番号をレジに提示することでお支払い頂けます。

トラザロン 50mg x 100錠
7,260円
ポイント:217pt
10,000円以上購入で送料無料
在庫あり

いつも不安に押しつぶされそうで、次の日が来るのが怖くて眠れなかった。睡眠不足になって体調も優れないから薬を飲むようになった。今は不安な気持ちがどっかいって、落ち着いて過ごせるようになってる。眠るのも怖くない。今はこの薬を手放すのが怖い。
トラザロンを飲むようになってから頭痛を感じることが多くなった。他の薬に変えてみたら頭痛は感じないから自分にはトラザロンが合わなかったみたい。
国立成育医療研究センターの研究グループが検討した結果では、薬の服用によって先天異常の発生率の上昇は認められなかったという結果が出ています。こうした結果は出ていますが、不明な部分もまだまだ多いため妊娠などを考えた場合には事前に医師に相談するなどして、指示を仰ぐようにしてください。
服用する治療薬の種類によって変わります。特定の治療薬では体重増加が副作用として報告されている数が多かったり、逆に体重の減少が副作用として報告されているものもあります。そのため、一概に太るということは言えません。
統合失調症の治療薬で脳が委縮するといったことはありません。脳の萎縮や機能低下は統合失調症の進行によっておきます。そのため、適切な治療をせずに放置していたり、自己判断で治療薬を中止したりした場合には、そうしたリスクは高くなると言えます。
統合失調症治療を薬で行い、その副作用が強くあらわれるというような場合には、医師に相談するようにしましょう。そうすることで内服する量を調整したり、服用する治療薬を変えて治療するといったことが可能になります。
治療薬を服用したとしても、統合失調症になってしまうということはありません。ただし、治療薬を服用する場合には、当然副作用などのリスクが生まれてくるので、統合失調症治療薬の副作用に悩まされるといった可能性は考えられます。
何かしらの治療法で改善する可能性はゼロではありません。ですが、統合失調症は原因は分かっておらず、適切な治療を行えていなければ、症状は進行していくだけになってしまい取り返しのつかない状態になる可能性も考えられるため現段階で有効とされる投薬治療を行う方がよいと考えられます。
| 1日の服用回数 | 1~数回 |
|---|---|
| 1日の服用量 | 75~200mgを分割 |
| 服用のタイミング | 指定なし |
| 服用間隔 | 6時間以上 |
| 商品名 | フルニル | フォンクセラ | セルティマ | セルタファイン | サミー | ティアプレックス | プロザック |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品画像 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 特徴1 | ・副作用や依存性が少ない | ・国内処方されている抗うつ薬のジェネリック | ・ゾロフトより安価 | ・憂うつな気分や不安感をやわらげる | ・もともと体内にある天然物質を配合 | ・さまざまな精神症状に応用されている有効成分を配合 | ・大手製薬会社イーライリリーが製造販売 |
| 特徴2 | ・プロザックよりも安価で大容量 | ・従来のSSRIより副作用が少ないとされている | ・様々なこころの不調に対して有効 | ・従来の抗うつ薬と比べて、口渇や便秘などの副作用が軽減されている | ・優れた抗酸化作用にも期待することができる | ・病院で処方されているグラマリール錠と同成分 | ・安価に試せるジェネリック医薬品フルニルもある |
| 内容量 | 10mgx100錠 | 5mg28錠x1箱 | 25mgx100錠 | 100mg100錠x1箱 | 200mgx30錠 | 25mg100錠x1箱 | 20mg28錠x1箱 |
| 価格 | 3,560円 | 4,860円 | 5,460円 | 6,260円 | 5,760円 | 4,160円 | 5,360円 |
本製品は海外製のため、期限表記が日本と異なる場合がございます。
パッケージ裏面や側面、シートなどに以下のような表記がされています。
| EXP | 使用期限 例:EXP 12/2025→2025年12月まで使用可 |
|---|---|
| MFG または MFD | 製造日 例:MFG 03/2023 |
| BEST BEFORE | 品質が最も安定している目安日 |
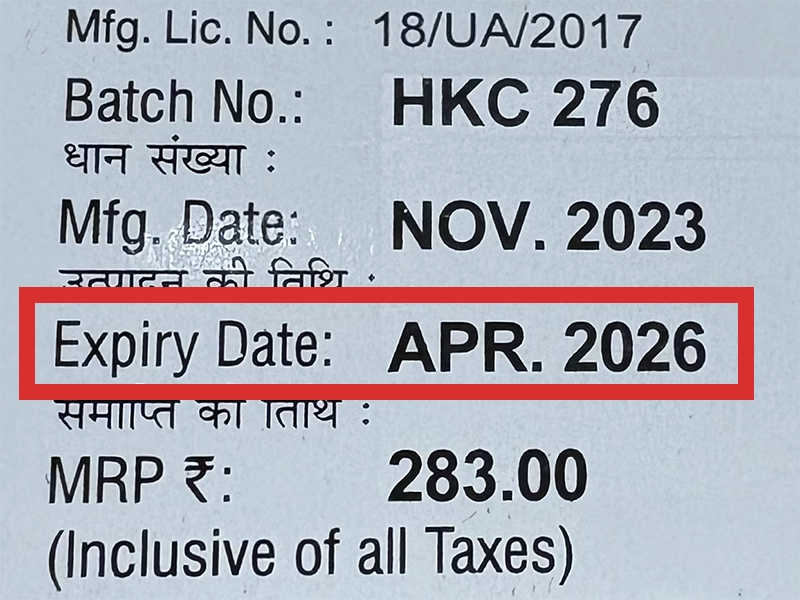
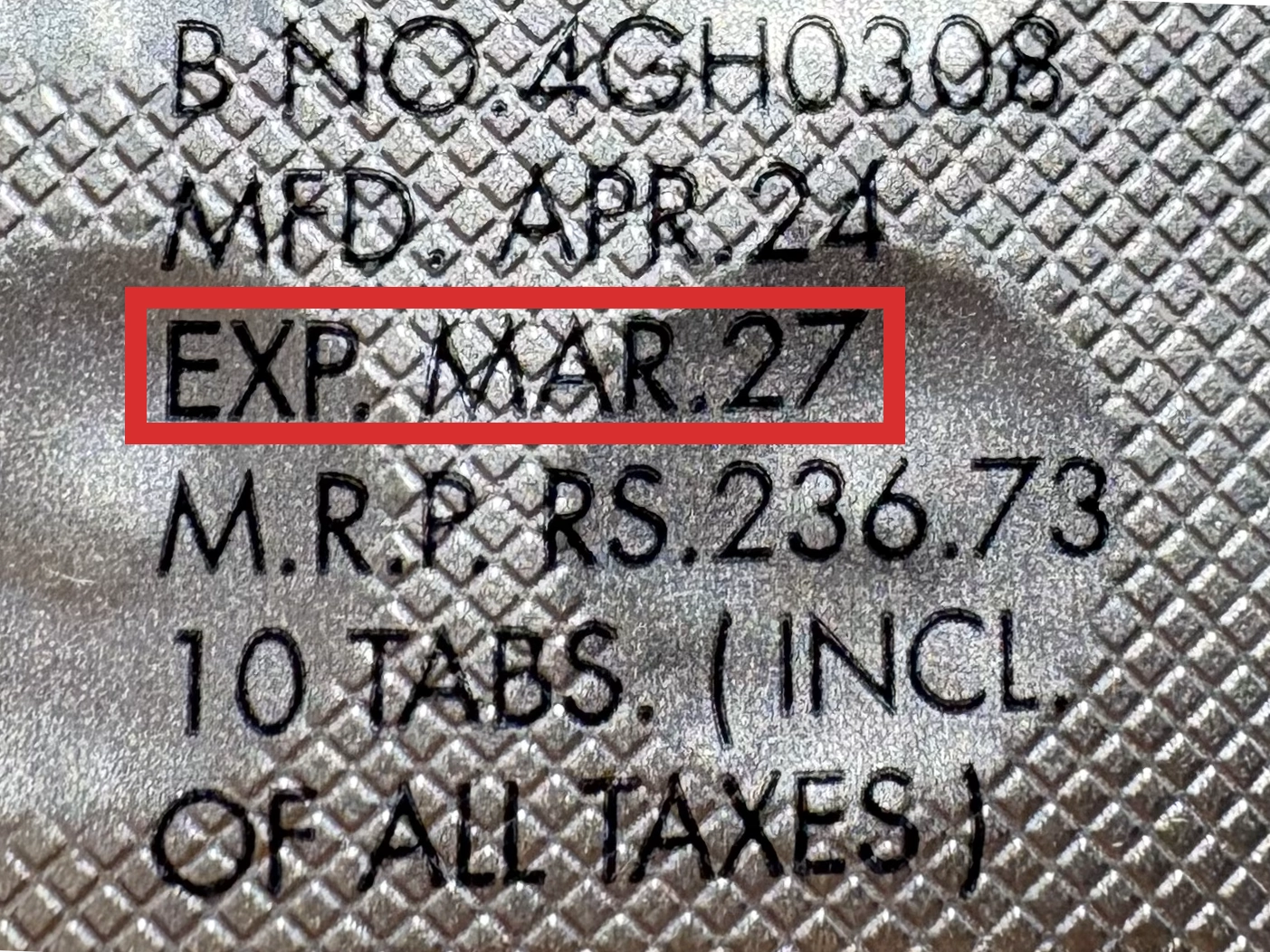
※国や製品により日付の並び(例:月/年、日/月/年)が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください
EXP(Expiry Date) の表記がなく、MFG または MFDしか記載がないケースがあります。
この場合は MFG(MFD) から2~3年が使用期限の目安です。
※「LOT」や「BATCH」の表記は製造番号であり期限ではありません。

パッケージ例となります。
商品やご注文単位によってはシート単位でのお届けとなる場合が御座います。
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。
気持ちが不安定な時に飲むと楽になれるし、スッと寝付けるようになる。軽い副作用は感じるけど自分はそこまで気にならない。
いつも不安に押しつぶされそうで、次の日が来るのが怖くて眠れなかった。睡眠不足になって体調も優れないから薬を飲むようになった。今は不安な気持ちがどっかいって、落ち着いて過ごせるようになってる。眠るのも怖くない。今はこの薬を手放すのが怖い。
眠くなる感じはわからないけどあれだけ不安症だった私が落ち着いて行動できるようになってるから効き目はいい!
トラザロンを飲むようになってから頭痛を感じることが多くなった。他の薬に変えてみたら頭痛は感じないから自分にはトラザロンが合わなかったみたい。
私は副作用を感じないので、ただただ睡眠の質が上がりメンタルを健全に保つことが出来てます。しっかりと効果を感じるの何回もリピートしてます!
商品口コミの投稿は会員のみ行えるようになっております。
お手数ですが会員ログインの上でご投稿頂きますようお願いいたします。
口コミをご投稿頂いたお客様にはポイントをプレゼントさせて頂いております。
文章のみであれば100ポイント、文章+写真付きのものは300ポイントをプレゼントさせて頂きます。
規約や詳細などはこちらをご確認くださいませ。