年齢と共に些細なことでカッとなりやすくなった気がしていました。この伝統的なハーブを試したら、以前より落ち着いて物事に対応できるようになった感じがします。

左記クレジットカード、銀行振込、コンビニ決済に対応


更新日:2025/6/19

| 個数 | 販売価格(1本あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1本 | 2,460円 | 2,460円 | 73pt | |
| 3本 | 1,320円 | 3,960円 | 118pt | |
| 5本 | 1,112円 | 5,560円 | 166pt |






①1万円以上で送料無料
1回の注文で10,000円以上だった場合、1,000円の送料が無料となります。
まとめ買いをすると1商品あたりのコストパフォーマンスが高くなるためおすすめです。
②プライバシー守る安心梱包
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。

③100%メーカー正規品取り扱い
当サイトの商品は100%メーカー正規品となっており、第三者機関による鑑定も行っております。
商品の破損などがあった場合は再配送などにて対応させて頂きますので、ご連絡頂ければ幸いです。

④いつでも購入可能 処方箋不要
サイト上では24時間いつでもご注文を受けております。
また、お電話によるご注文も受け付けておりますのでネットが苦手な方はお気軽にどうぞ。

⑤商品到着100%
商品発送後はお荷物の追跡状況が分かる追跡番号をご案内させて頂きます。
郵便局には保管期限がありますのでご注意ください。
・自宅配達で不在だった場合の保管期限・・・16日間前後
・郵便局留めとした場合の保管期限・・・7~30日間

⑥コンビニ決済利用可能
ご近所のコンビニにていつでもお支払可能です。
セブンイレブンに限り店舗での機械操作を必要とせず、手続き完了後に表示されるバーコードや払込票番号をレジに提示することでお支払い頂けます。

セルピナ 100錠 x 1本
2,460円
ポイント:73pt
10,000円以上購入で送料無料
在庫あり

年齢と共に些細なことでカッとなりやすくなった気がしていました。この伝統的なハーブを試したら、以前より落ち着いて物事に対応できるようになった感じがします。
サプリなので飲んで体調が悪くなってしまうことは一切なかったです。でもその分効果がゆるすぎるというか、何も実感できてないなぁという印象です。血圧もこれで結構下がるらしいのですが、私はこの前健康診断を受けてみたらそこまで変わってませんでした。もっと飲み続けていく必要があるのかもしれない。それとも体と合わないのかな。その辺すらも、自分ではよくわかりません。
| 1日の服用回数 | 2回 |
|---|---|
| 1回の服用量 | 1錠 |
| 服用のタイミング | 指定なし |
| 服用間隔 | 指定なし |
| 商品名 | ブロプレス | オルメタイム | サイアムドパ | ノルバスク | カバーヒール | アクテル |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品画像 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 特徴1 | ・心臓病や腎臓病にも有効 | ・2つの有効成分で高い効果が期待できる | ・交感神経に作用して血圧を下げる | 有効成分がゆるやかに血圧を下げる | ・血糖や尿酸、脂質などに影響を与えない | ・日本国内で処方されているコナン錠の海外版 |
| 特徴2 | ・症状に応じて用量を選べる | ・比較的副作用が少ない降圧剤 | ・糖尿病がある方や妊娠中でも服用できる | 安心して使える大手メーカー製 | ・予後改善効果が臨床試験で証明されている | ・年齢を問わずに広く使うことができる |
| 内容量 | 4mgx30錠 | 30錠x1箱 | 125mg100錠x1箱 | 5mgx30錠 | 4mg100錠x1箱 | 5mg20錠x1箱 |
| 価格 | 4,360円 | 4,060円 | 4,160円 | 4,160円 | 3,000円 | 2,500円 |
本製品は海外製のため、期限表記が日本と異なる場合がございます。
パッケージ裏面や側面、シートなどに以下のような表記がされています。
| EXP | 使用期限 例:EXP 12/2025→2025年12月まで使用可 |
|---|---|
| MFG または MFD | 製造日 例:MFG 03/2023 |
| BEST BEFORE | 品質が最も安定している目安日 |
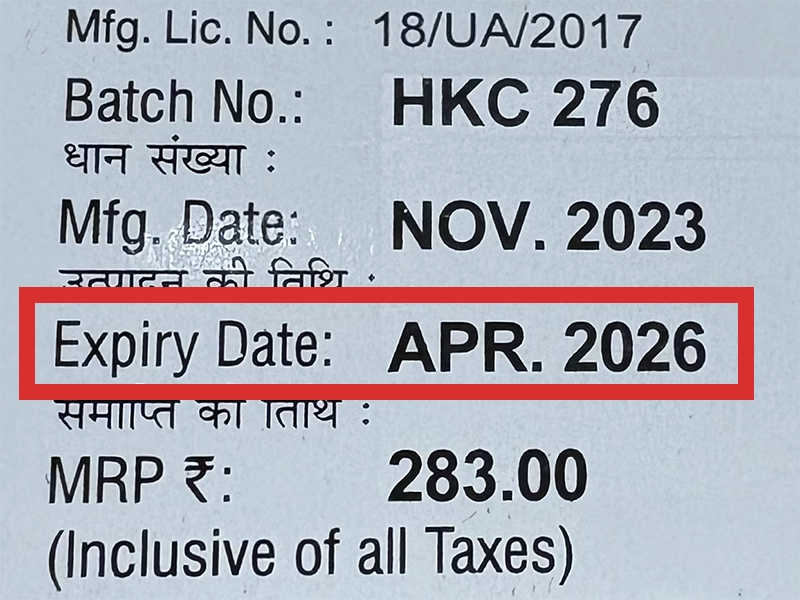
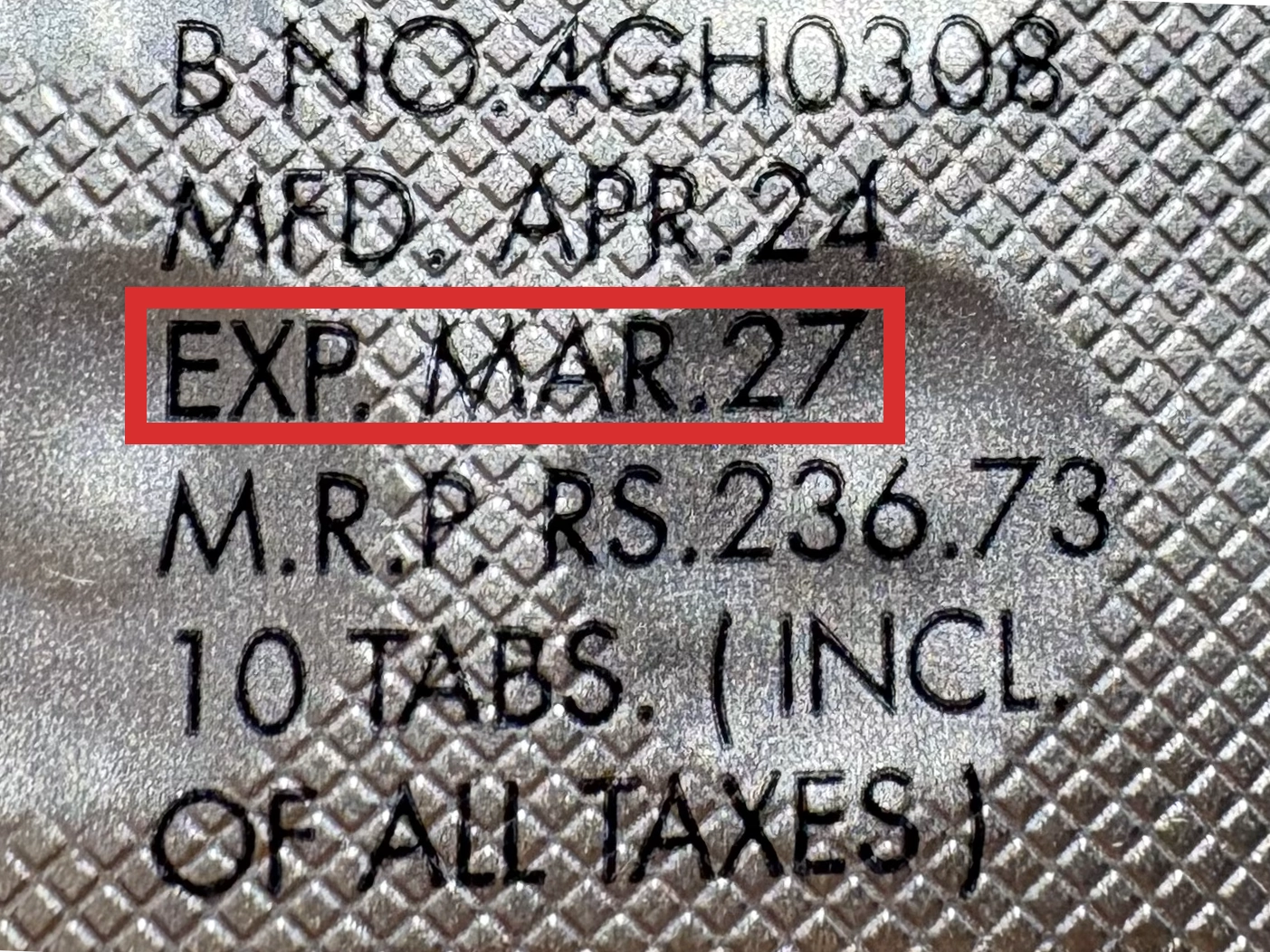
※国や製品により日付の並び(例:月/年、日/月/年)が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください
EXP(Expiry Date) の表記がなく、MFG または MFDしか記載がないケースがあります。
この場合は MFG(MFD) から2~3年が使用期限の目安です。
※「LOT」や「BATCH」の表記は製造番号であり期限ではありません。

パッケージ例となります。
商品やご注文単位によってはシート単位でのお届けとなる場合が御座います。
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。
更年期に入りイライラや不眠症などの症状が出てくるようになり、こちらのサプリメントを利用するようになりました。リラックス感や寝付きがよくなって睡眠の質が高くなっている事を実感しています。サプリなんで副作用なども感じないのも良い点ですね。
日々のストレスでイライラしがちで、夜も考え事をして寝付けないことがありました。これを飲むようになってから、気持ちが穏やかになり、リラックスできる時間が増えた気がします。寝つきも少し良くなりました。
年齢と共に些細なことでカッとなりやすくなった気がしていました。この伝統的なハーブを試したら、以前より落ち着いて物事に対応できるようになった感じがします。
これはすごくいいですね。不安感やイライラ感が一気に消えたように感じます。また、睡眠の時間も安定するようになりました。飲むまでは2、3時間しか眠れない日がけっこうあって疲れが全然取れないような状態でしたが、今は7時間くらいは必ず眠れるようになりました。サプリメントを飲むだけでこんなに変わると思っていませんでした。また引き続いて購入したいと思いました。
もともとの血圧が高いので、セルピナのようなサプリメントをよく愛用しています。セルピナのおかげで、医師から血圧の注意を受けることが減りました。それだけじゃなく、急にイライラしたりもやもやしたりすることが多かった精神状態も整えてくれているらしいです。最近は調子が良さそうだと家族にも言われました。近々また買うかもしれません。
商品口コミの投稿は会員のみ行えるようになっております。
お手数ですが会員ログインの上でご投稿頂きますようお願いいたします。
口コミをご投稿頂いたお客様にはポイントをプレゼントさせて頂いております。
文章のみであれば100ポイント、文章+写真付きのものは300ポイントをプレゼントさせて頂きます。
規約や詳細などはこちらをご確認くださいませ。