本来は皮膚組織や貧血のための薬のようですが、筋力増加用の薬としても十分役立ちます。皮膚組織の再生に元々効果があるので、皮膚組織の再生力も高まっている気がします。怪我に強くなりながら筋力アップを狙えます。

左記クレジットカード、銀行振込、コンビニ決済に対応


更新日:2025/6/22

| 個数 | 販売価格(1錠あたり) | 販売価格(箱) | ポイント | 購入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60錠 | 97円 | 5,860円 | 175pt | |
| 120錠 | 84円 | 10,160円 | 304pt |






①1万円以上で送料無料
1回の注文で10,000円以上だった場合、1,000円の送料が無料となります。
まとめ買いをすると1商品あたりのコストパフォーマンスが高くなるためおすすめです。
②プライバシー守る安心梱包
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。

③100%メーカー正規品取り扱い
当サイトの商品は100%メーカー正規品となっており、第三者機関による鑑定も行っております。
商品の破損などがあった場合は再配送などにて対応させて頂きますので、ご連絡頂ければ幸いです。

④いつでも購入可能 処方箋不要
サイト上では24時間いつでもご注文を受けております。
また、お電話によるご注文も受け付けておりますのでネットが苦手な方はお気軽にどうぞ。

⑤商品到着100%
商品発送後はお荷物の追跡状況が分かる追跡番号をご案内させて頂きます。
郵便局には保管期限がありますのでご注意ください。
・自宅配達で不在だった場合の保管期限・・・16日間前後
・郵便局留めとした場合の保管期限・・・7~30日間

⑥コンビニ決済利用可能
ご近所のコンビニにていつでもお支払可能です。
セブンイレブンに限り店舗での機械操作を必要とせず、手続き完了後に表示されるバーコードや払込票番号をレジに提示することでお支払い頂けます。

オキシポロン 50mg x 60錠
5,860円
ポイント:175pt
10,000円以上購入で送料無料
在庫あり

本来は皮膚組織や貧血のための薬のようですが、筋力増加用の薬としても十分役立ちます。皮膚組織の再生に元々効果があるので、皮膚組織の再生力も高まっている気がします。怪我に強くなりながら筋力アップを狙えます。
副作用を我慢しながら使っていましたが、ほとんど効果がありませんでした。最近の海外医薬品は効果が高いものとばかり思っていましたが、そんなことない医薬品もまだあるんですね・・・。次はもっと慎重に選びたいと思います。
アナボリックステロイドを服用することによって、テストステロンの分泌が減少してしまいます。その結果、精子の産生が減少してしまいます。精子の産生が減少してしまうことで子供ができる確率は下がってしまいます。ただし、完全にゼロとなってしまうわけではないため、子作りは不可能ではありません。
アナボリックステロイドの効果については、配合成分によって作用のアプローチにも違いがあるためです。ダイエット向きとされるものの成分は水分の貯留であったり、副作用が少ないといったことが挙げられています。こうしたことから、目的に合わせて使用するものを選ぶのも有効です。
アナボリックステロイドの使用を辞めることは可能です。ただし、その場合、ステロイドによって筋肥大がステロイド未使用の限界をこえているような状態を維持することはできません。そのため、ステロイドを使用せずにトレーニングしている状態をこえた筋肉量を維持したいと考えている場合には継続しての使用などが必要になります。
アナボリックステロイドの錠剤と注射で効果に違いはありません。筋力量の増加を促進することで、筋肥大などに期待することが可能となっています。
アナボリックステロイドは蛋白同化作用を持っているため、効果的な筋力増強を可能にします。一方でプロテインは栄養素であるタンパク質を効率的に補う健康食品であるため、プロテインそのものに筋力増強の作用はありません。そのため、筋力増強の効果という点で考えると、アナボリックステロイドの方が効果があると言えます。
| 1日の服用回数 | 2~4回 |
|---|---|
| 1日の服用量 | 体重1kgに対し1~5mg |
| 服用のタイミング | 食後、食事と共に |
| 服用間隔 | 指定なし |
| 商品名 | スタノゾロール | アナドリン | メダナボル | ウィンゾロン | ハロフルオックス | プリモノロン | アンドロフォルテクリーム | テストステロンジェル |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品画像 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 特徴1 | 筋肉や骨を強くする有効成分を配合 | ・骨髄の機能を高める効果にも期待できる | 効率よく筋肉増強をサポートする | 実績のある筋肉増強剤 | ・体脂肪を減らす効果にも期待できる | ・女性化作用や肝臓への負担が少ない | ・手軽に男性ホルモンを補給できる | 男性ホルモン補充で筋肉増強 |
| 特徴2 | 造血力UPにより貧血改善にも期待できる | ・カルシウムの排出量を抑えて骨を強化する | ボトル1本にたっぷり60錠入り | 大容量(150錠)入りボトル | ・服用を中止しても一定期間、効果が持続する | ・従来の筋肉増強剤より安全性が高い | ・さっと使用することができる外用薬タイプ | 皮膚から直接有効成分を取り込めるクリーム |
| 内容量 | 2mgx20錠 | 10mgx60錠 | 10mgx60錠 | 10mgx150錠 | 5mgx120錠 | 25mgx150錠 | 5%x1箱 | 1% 5gx1本 |
| 価格 | 2,760円 | 6,260円 | 4,360円 | 6,060円 | 14,060円 | 29,160円 | 24,460円 | 1,800円 |
本製品は海外製のため、期限表記が日本と異なる場合がございます。
パッケージ裏面や側面、シートなどに以下のような表記がされています。
| EXP | 使用期限 例:EXP 12/2025→2025年12月まで使用可 |
|---|---|
| MFG または MFD | 製造日 例:MFG 03/2023 |
| BEST BEFORE | 品質が最も安定している目安日 |
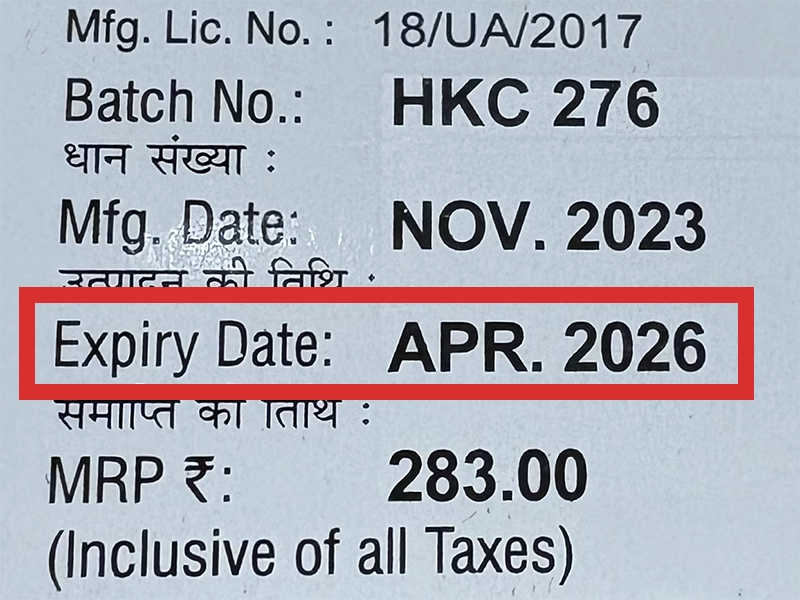
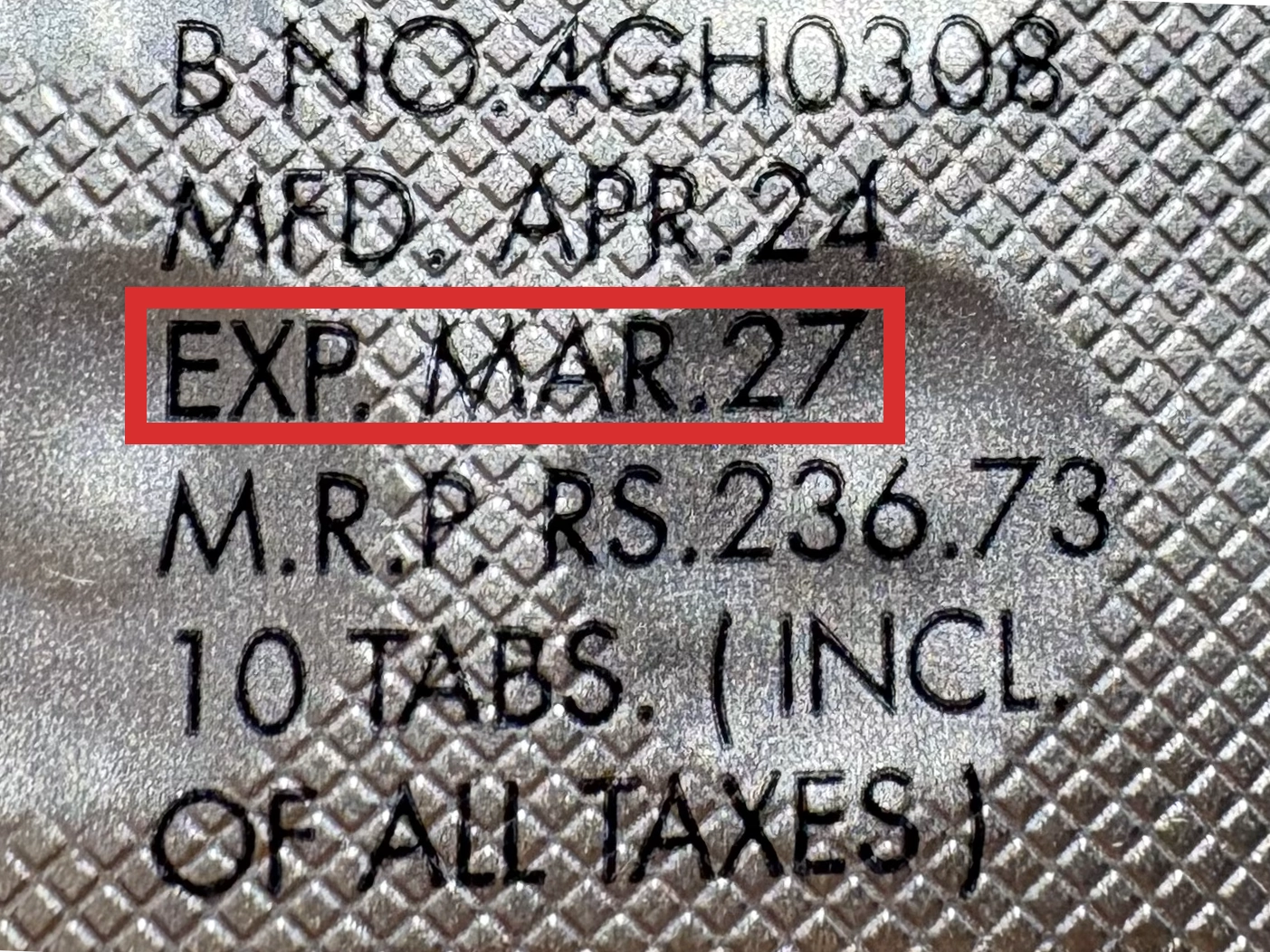
※国や製品により日付の並び(例:月/年、日/月/年)が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください
EXP(Expiry Date) の表記がなく、MFG または MFDしか記載がないケースがあります。
この場合は MFG(MFD) から2~3年が使用期限の目安です。
※「LOT」や「BATCH」の表記は製造番号であり期限ではありません。

パッケージ例となります。
商品やご注文単位によってはシート単位でのお届けとなる場合が御座います。
外箱に当サイト名や商品名が記載されることはないため、ご家族や配達員など第三者に内容を知られることは御座いません。
筋力増加に効果的な薬は他にもありますが、これが一番副作用なく使えました!他の製品だと副作用だらけでトレーニングどころじゃなくなることも多いだけに、これは本当に感動しました。おかげで少しずつですが、筋肉もついてきました。
昔から続く貧血気味を解消するために飲んでいます。サプリよりも効果的に血液の健康を保てているように感じます。造血作用もあるそうですし、これでなんとか貧血気味が解消されてほしいです。期待を込めての星4です。
副作用を我慢しながら使っていましたが、ほとんど効果がありませんでした。最近の海外医薬品は効果が高いものとばかり思っていましたが、そんなことない医薬品もまだあるんですね・・・。次はもっと慎重に選びたいと思います。
短期間で効率よく体を引き締められそうだからセレクト。やや食欲が落ちた感覚はあるが、体を引き締めるつもりで買ったから逆にちょうどよさそう。体重が減るか、筋肉がついてくるか、どちらかの効果が出てきたら引き続き使っていきたい。今のところは変化なし。
飲んでいたら、だんだん体がだるくなり、怖くなってきた段階で服用中止。調べてみれば、倦怠感が副作用の欄の中に。あれは副作用が出てたんだなと納得したが、副作用が出る薬はやっぱり不安になる。
商品口コミの投稿は会員のみ行えるようになっております。
お手数ですが会員ログインの上でご投稿頂きますようお願いいたします。
口コミをご投稿頂いたお客様にはポイントをプレゼントさせて頂いております。
文章のみであれば100ポイント、文章+写真付きのものは300ポイントをプレゼントさせて頂きます。
規約や詳細などはこちらをご確認くださいませ。